Some links on our blog are affiliate links, meaning at no extra cost to you, we may earn a commission if you purchase through them. We participate in the Amazon Affiliate Program, and we recommend products we believe in. Your support helps us keep providing valuable content. Thank you!
Pregnancy “lingo” encompasses a variety of terms, abbreviations, and slang that are commonly used by healthcare providers, expectant parents, and in online forums or support groups related to pregnancy. These terms help streamline communication and offer a shorthand for complex medical terms or common experiences related to pregnancy.
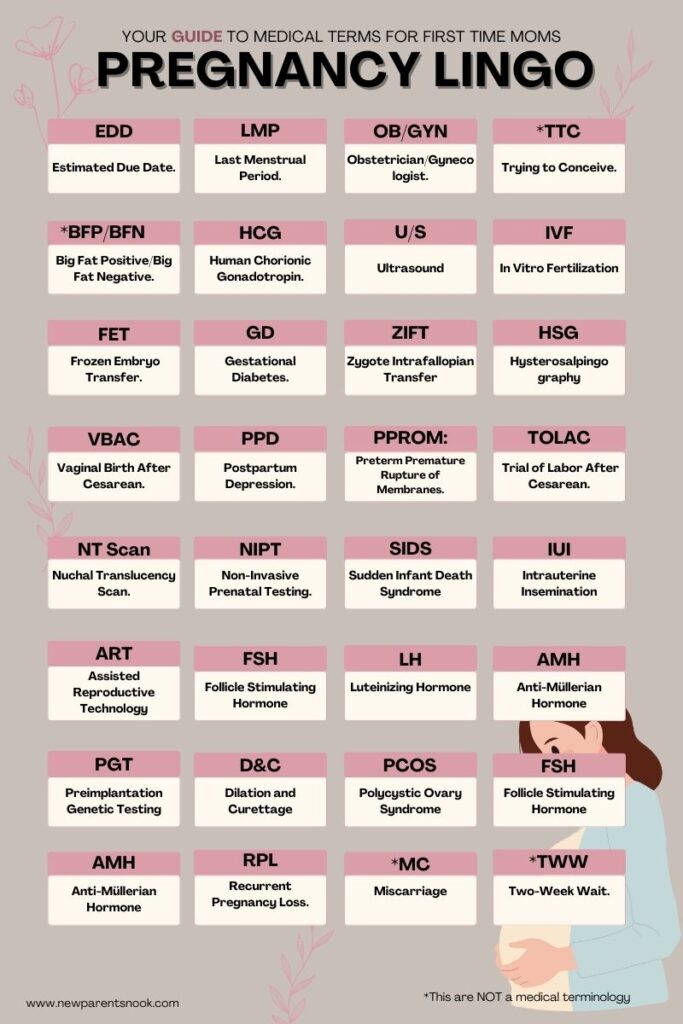
Here are some of the most common terms and their meanings:
- EDD: Estimated Due Date. The calculated date when the baby is expected to be born.
- LMP: Last Menstrual Period. The first day of the last menstrual cycle, used to calculate the EDD.
- OB/GYN: Obstetrician/Gynecologist. A doctor specializing in pregnancy, childbirth, and the reproductive system of women.
- TTC: Trying to Conceive. Refers to individuals or couples who are attempting to get pregnant.
- BFP/BFN: Big Fat Positive/Big Fat Negative. Terms used in pregnancy tests. BFP means a positive pregnancy test, while BFN means a negative result.
- HCG: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. A hormone produced during pregnancy, which is detected by pregnancy tests.
- U/S: Ultrasound. A medical test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the baby and uterus.
- IVF: In Vitro Fertilization. A process by which an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body, and then the fertilized egg (embryo) is transferred to the uterus.
- FET: Frozen Embryo Transfer. A process in IVF where a cryopreserved embryo is thawed and transferred to the uterus.
- GD: Gestational Diabetes. A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after giving birth.
- VBAC: Vaginal Birth After Cesarean. Referring to delivering a baby vaginally after having a previous baby by cesarean section.
- PPD: Postpartum Depression. A type of depression that can occur after childbirth.
- LO: Little One. A term of endearment for a baby or child.
- TWW: Two-Week Wait. The period between ovulation and when a woman can realistically take a pregnancy test to determine if she is pregnant.
- NT Scan: Nuchal Translucency Scan. A prenatal test conducted in the first trimester to assess the risk of Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
- NIPT: Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing. A blood test that can detect certain genetic conditions as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy.
- IVF: In Vitro Fertilization. A process where an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body, in a lab, and then the embryo is transferred to the uterus.
- IUI: Intrauterine Insemination. A fertility treatment that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilization.
- ART: Assisted Reproductive Technology. All treatments that involve handling eggs or embryos outside of the body, including IVF, IUI, and third-party reproduction.
- FSH: Follicle Stimulating Hormone. A hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that plays a crucial role in controlling the menstrual cycle and stimulating the growth of eggs in the ovaries.
- LH: Luteinizing Hormone. A hormone that triggers ovulation and the development of the corpus luteum.
- AMH: Anti-Müllerian Hormone. A hormone secreted by the ovaries that can give an indication of a woman’s ovarian reserve or the number of remaining eggs.
- PPROM: Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes. This refers to the breaking of the water (amniotic sac) before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- TOLAC: Trial of Labor After Cesarean. An attempt to have a vaginal birth after a cesarean section in a previous pregnancy.
- GBS: Group B Strep. A type of bacterial infection that can be found in a pregnant woman’s vagina or rectum. Women are typically tested for GBS late in pregnancy because it can be harmful to the baby during delivery.
- SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. While not a pregnancy term per se, it’s often discussed in prenatal classes and literature. SIDS is the unexplained death, usually during sleep, of a seemingly healthy baby less than a year old.
- PGT: Preimplantation Genetic Testing. A procedure used to identify genetic defects in embryos created through IVF before pregnancy.
- MC: Miscarriage. The loss of a pregnancy before the fetus is viable outside the womb, typically defined as before 20 weeks of gestation.
- PCOS: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. A hormonal disorder causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges, often leading to infertility issues.
- RPL: Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. The occurrence of three or more consecutive pregnancy losses before 20 weeks of gestation.
- ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer): A fertility treatment where a fertilized egg is placed into the fallopian tube rather than the uterus.
- HSG (Hysterosalpingography): An X-ray test that looks at the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes and the area around them, often used to investigate blockages that could affect fertility.
- D&C (Dilation and Curettage): A surgical procedure often performed after a miscarriage or for diagnostic purposes. During a D&C, the cervix is dilated, and a special instrument is used to scrape the uterine lining to remove tissue.
helpful and informative terminology (Pregnancy related)
These terms cover aspects of medical diagnoses, treatment procedures, tests, and emotional experiences related to pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum period and infertility. Here’s a list of key terms and their definitions:
- Kick Count: A method used by expectant mothers to monitor their baby’s activity levels by counting the number of kicks or movements felt within a certain time period, often recommended in the third trimester.
- Braxton Hicks Contractions: Often referred to as “practice contractions,” these are irregular, usually painless contractions that occur throughout pregnancy. They are not a sign of labor.
- Amniocentesis: A medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis, where a small amount of amniotic fluid is sampled from the amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus. It can provide information about the baby’s health.
- Epidural: A form of anesthesia used during labor to reduce pain in the lower part of the body.
- Linea Nigra: A dark vertical line that appears on the abdomen during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
- Mucus Plug: A plug of mucus that blocks the cervical canal during pregnancy, providing protection against infection. It is often expelled just before or during labor.
- Nesting: An urge to clean and organize one’s home before the arrival of the baby, often seen as an instinctual behavior that signals the approach of labor.
- Surfactant: A substance that helps keep the air sacs in the lungs from sticking together. It is particularly important for premature babies, as their lungs may not have produced enough surfactant yet.
- Preeclampsia: A pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, most often the liver and kidneys.
- Skin to Skin: A practice where a baby is dried and laid directly on the mother’s bare chest after birth, which can help regulate the baby’s temperature and heart rate, encourage bonding, and initiate breastfeeding
- Infertility: The inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse, or the inability to carry a pregnancy to term.
- Reserve: The capacity of the ovary to provide egg cells that are capable of fertilization resulting in a healthy and successful pregnancy.
- Semen Analysis: A test that evaluates the quantity and quality of a man’s semen and sperm to assess his fertility.
- Embryo Transfer: The process of placing an embryo into a woman’s uterus or the uterus of a surrogate mother, hoping it will implant and result in a pregnancy.
- Cryopreservation: The process of freezing eggs, sperm, or embryos for future use.
- Surrogacy: An arrangement where a woman agrees to carry and deliver a child for another person or couple.
- Egg Donation: A process where eggs are donated by one woman (the donor) to another (the recipient), typically involving IVF to facilitate the pregnancy.
- Sperm Donation: A process where sperm are donated by a man (the donor) to assist an individual or couple in achieving pregnancy.
- Secondary Infertility: The inability to become pregnant or to carry a pregnancy to term after previously giving birth to a child or children.
- Endometriosis: A condition in which tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus is found outside the uterus, causing pain and potentially affecting fertility.
- Tubal Factor Infertility: Infertility resulting from damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes, which prevents the egg from being fertilized or the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus.
- Sperm Motility: The ability of sperm to move efficiently. This is important for fertility because sperm need to navigate through the female reproductive tract to reach and fertilize an egg.
- Sperm Morphology: The shape and structure of sperm. Abnormal morphology may impair the ability of sperm to fertilize an egg.
- Blastocyst: A stage of embryo development, typically reached five to six days after fertilization, when the embryo has divided many times and is ready for implantation in the uterine lining.
- Egg Retrieval: A procedure in IVF where eggs are collected from the ovaries with a needle guided by ultrasound.
- Assisted Hatching: A laboratory technique used in IVF where the outer shell of the embryo (the zona pellucida) is thinned or breached to assist the embryo in breaking out (hatching) and implanting in the lining of the uterus.
- Male Factor Infertility: Infertility due to low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology.
- Ovulation Induction: The use of medications to stimulate ovulation in women who do not ovulate regularly or at all.
- Sperm Analysis: A test to measure the quantity and quality of a man’s sperm.
- Zygote: The cell formed by the combination of a sperm and an egg at fertilization.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy in which the embryo implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. It’s a serious condition that can cause significant health risks to the mother.
- Luteal Phase: The phase of the menstrual cycle that begins after ovulation and ends with the start of menstruation. It’s when the body prepares for a possible pregnancy, and a key focus in infertility discussions for its length and hormonal environment being crucial for implantation and early pregnancy maintenance.
These terms represent just a portion of the extensive vocabulary associated with TTC. Understanding these terms can help individuals and couples navigate their fertility journey more effectively.